Ant Patterns: Unlocking Secrets for Better Fly Fishing Flies
Ants, with their miniature size, exhibit complex behaviors that have fascinated scientists and inspi…….
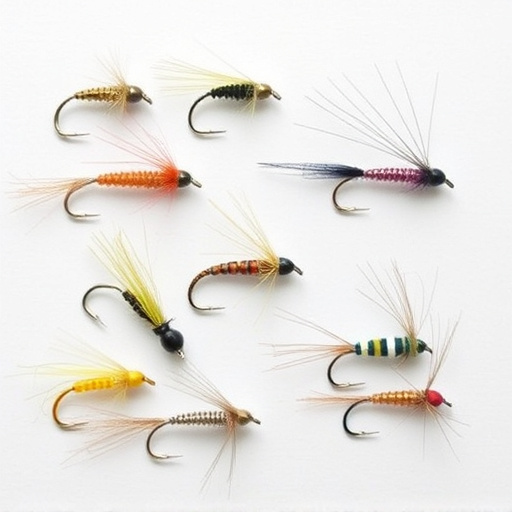

Ants, with their miniature size, exhibit complex behaviors that have fascinated scientists and inspired innovations. Through pheromone communication, they display sophisticated colony dynamics, from foraging to defense, showcasing remarkable efficiency known as swarm intelligence. This behavior has directly influenced fly fishing techniques, where synthetic pheromone-imitating fly fishing flies attract specific fish species by mimicking natural cues. By observing ant structures (monogene vs polygene) and movements, anglers can optimize their strategies, improving catch rates through precise fly placement and realistic presentations.
Ant patterns offer fascinating insights into nature’s intricate strategies. This article explores the complex world of ants, delving into their understanding, behavior, and communication methods. We uncover the crucial role of pheromones in their navigation and social interactions, revealing how these chemical signals mimic the effects of fly fishing flies. Furthermore, we categorize different ant colony types and their behaviors, providing a comprehensive guide to enhancing fly fishing techniques with ant knowledge.
- Understanding Ant Behavior: Unveiling the Basics of Ant Patterns
- The Role of Pheromones in Ant Communication and Fly Fishing Flies
- Different Types of Ant Colonies and Their Unique Behaviors
- Utilizing Ant Knowledge for Effective Fly Fishing Techniques
Understanding Ant Behavior: Unveiling the Basics of Ant Patterns

Ants, despite their tiny size, exhibit complex and organized behaviors that have fascinated scientists for centuries. Understanding ant patterns is like deciphering a intricate dance—each ant follows specific rules within its colony, contributing to the overall success of the group. These social insects communicate through pheromones, leaving chemical trails much like a fly fishing enthusiast traces streams with their flies. Each path they create reveals the location of food sources, nest sites, or potential dangers.
By observing these patterns, researchers can uncover the fundamental principles of ant organization. From foraging to nesting and defense, ants coordinate their activities in a way that optimizes efficiency. This coordinated behavior, often referred to as swarm intelligence, has inspired various fields, from robotics to computer science, seeking to replicate these natural solutions.
The Role of Pheromones in Ant Communication and Fly Fishing Flies

Ants are renowned for their complex social structures and efficient communication systems, which are largely facilitated by pheromones. These chemical signals play a pivotal role in various ant behaviors, including recruitment to food sources and nest construction. When an ant discovers a promising meal, it returns to its colony and leaves a trail of pheromones, known as a scent trail, which guides other ants towards the food. This behavior is not just observed in nature but also serves as inspiration for innovative applications in fly fishing flies.
In the context of fly fishing, the concept of using pheromones has gained interest due to their ability to attract and entice specific species of fish. Fly fishing flies designed with synthetic pheromone imitations can mimic natural substances that trigger a fish’s instinctive response. This strategy enhances the effectiveness of lures, creating more successful catches. By understanding and harnessing the power of ant communication through pheromones, anglers can explore new techniques to improve their fly fishing experience, targeting specific species with greater precision.
Different Types of Ant Colonies and Their Unique Behaviors

Ant colonies come in various forms, each with its own specialized behaviors and structures. One of the most well-known is the monogene colony, characterized by a single queen and her workers. These colonies are highly organized, with distinct roles for each ant, much like a tightly orchestrated dance. The queen’s primary role is to lay eggs, ensuring the colony’s survival and growth. Workers, on the other hand, perform tasks such as foraging for food (similar to how anglers carefully select fly fishing flies for different water conditions), nurturing the young, and protecting the nest.
Another type is the polygene colony, where multiple queens exist within a single nest. This structure allows for greater genetic diversity but can lead to intense competition between queens. Each queen has her own set of workers, and they may specialize in different tasks or even fight over resources. This dynamic contrasts with the monogene colonies’ more harmonious division of labor. Such variations in ant colony types highlight the incredible adaptability and complexity of these tiny creatures, often overlooked yet crucial contributors to their ecosystems, much like how a skilled angler must adapt their fly fishing techniques to different river conditions.
Utilizing Ant Knowledge for Effective Fly Fishing Techniques

Ants, with their intricate foraging behaviors and complex social structures, offer valuable insights into the art of fly fishing. Observing ant colonies can teach anglers about habitat preferences and food sources of various species, helping them target specific fish. For instance, knowing where ants are active can indicate areas where certain fly fishing flies will be most effective. By mimicking these tiny creatures’ movements and patterns, anglers can create more realistic presentations that entice fickle fish.
Moreover, ant knowledge allows anglers to refine their casting techniques and line control. Understanding the speed and rhythm of ant movements inspires more precise casts, enabling fishermen to place their flies with greater accuracy. This precision is crucial for success in fly fishing, where subtle presentations often make the difference between a bite and a blank.
Ant patterns and behaviors offer a fascinating glimpse into nature’s intricate communication systems, with pheromones playing a pivotal role. Understanding these tiny creatures’ dynamics can significantly enhance fly fishing techniques, especially when considering the diverse colony structures and their specific habits. By recognizing ant behavior, anglers can refine their approach to fly fishing, making each cast more effective, particularly when targeting specific species influenced by these intricate ant patterns.